Math Series Example
This is a starter example using the aicuflow python library.
It creates a flow in your user account and streams data to a file in its file manager.
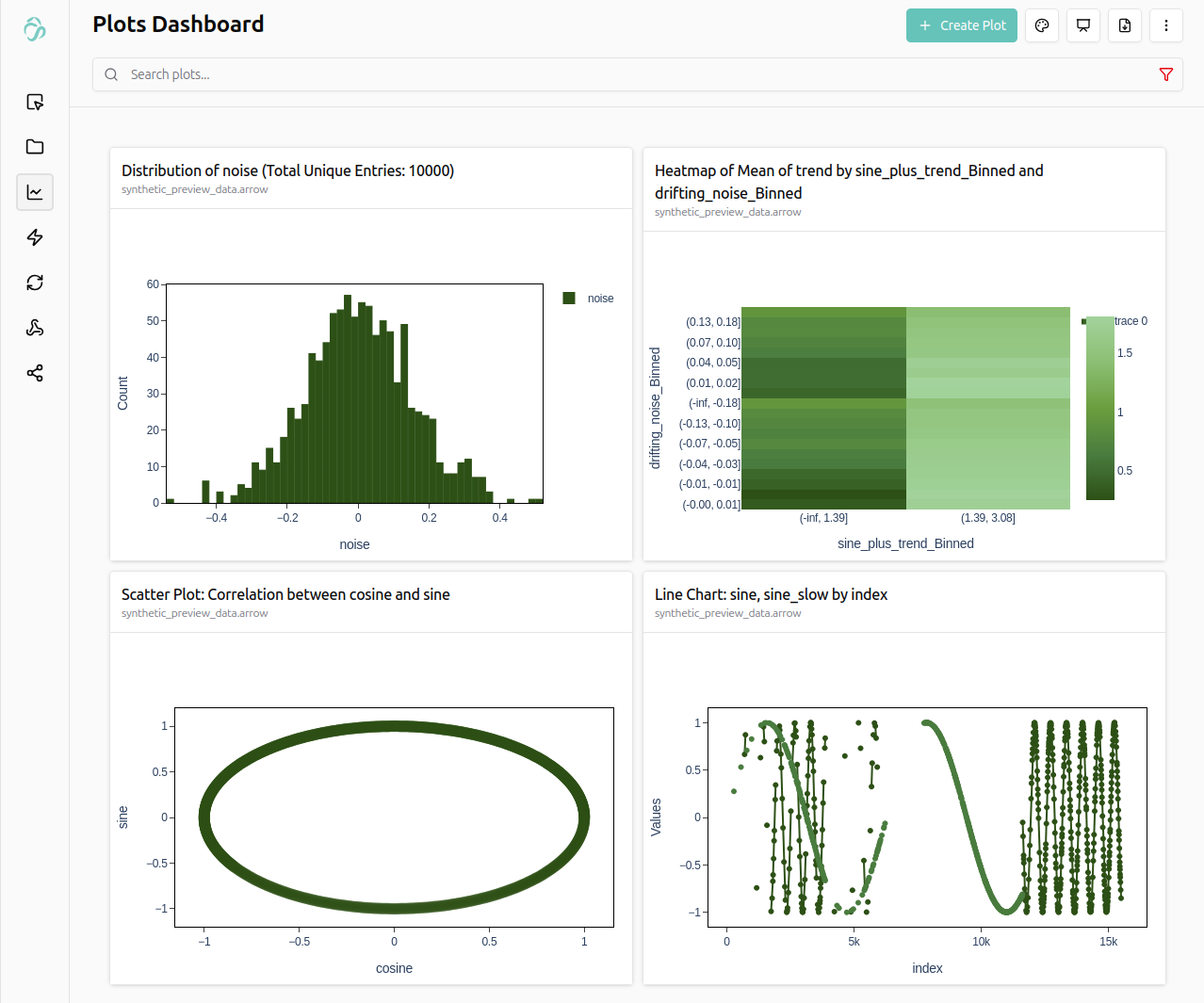
Copy the code below and run it for example in jupyterlab for testing.
import math
import time
import random
import aicuflow
# initialise aicuflow
ai = aicuflow.client(
email="YOUR_EMAIL",
password="YOUR_PASSWORD"
)
flow = ai.ensure_flow_by_title("basic math example")
file = aicuflow.file.byname(ai, flow, "synthetic_preview_data.arrow")
TOTAL_ROWS = 10_000
BATCH_SIZE = 500
buffer = []
start_time = time.time()
for i in range(TOTAL_ROWS):
t = i * 0.01
noise = random.gauss(0.0, 0.15)
sine = math.sin(t)
cosine = math.cos(t)
sine_slow = math.sin(t * 0.1)
sine_fast = math.sin(t * 3.0)
trend = 0.002 * i
scatter = random.random() - 0.5
drifting_noise = noise * math.sin(t * 0.3)
row = {
"index": i,
"time": start_time + t,
"const_one": 1.0,
"linear": i,
"linear_norm": i / TOTAL_ROWS,
"sine": sine,
"cosine": cosine,
"sine_slow": sine_slow,
"sine_fast": sine_fast,
"trend": trend,
"sine_plus_trend": sine + trend,
"noise": noise,
"scatter": scatter,
"sine_noise": sine + noise,
"cosine_noise": cosine + noise,
"drifting_noise": drifting_noise,
"modulated": sine * (1.0 + noise),
"envelope": sine * (0.5 + 0.5 * sine_slow),
}
buffer.append(row)
if len(buffer) == BATCH_SIZE:
file.append(buffer)
buffer.clear()
if buffer:
file.append(buffer)You find more examples in the python library examples.