Git Statistics Example
This is an advanced example using the aicuflow python library.
It creates a flow in your user account and streams git contribution data to a file in its file manager.
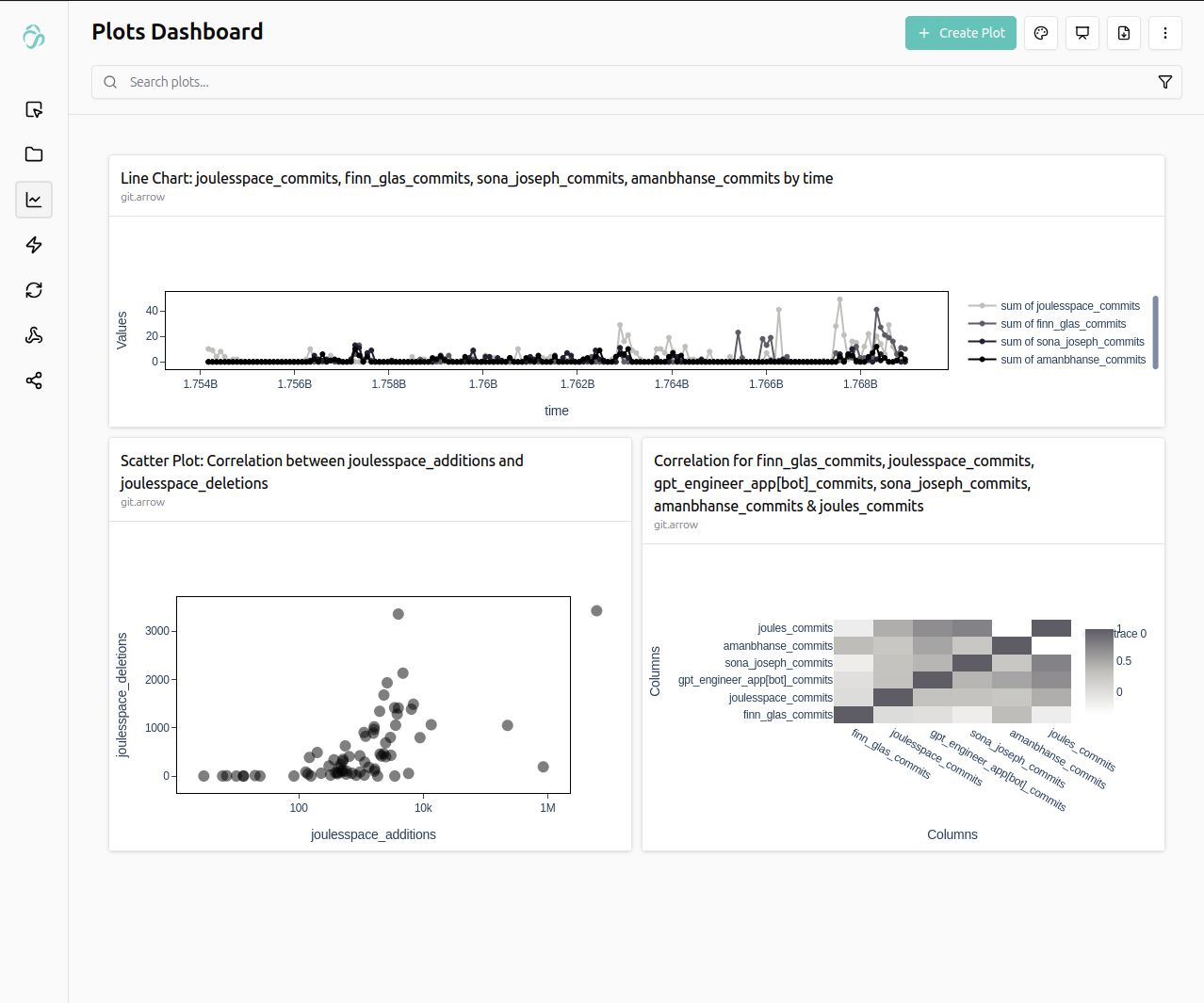
With this example, you can analyze the contributions of your teammates on your git repositories.
The above example data shown is taken from our frontend-teams performance between October 2025 and February 2026.
To understand the data insights, let's use the present mode with the correlation plot:
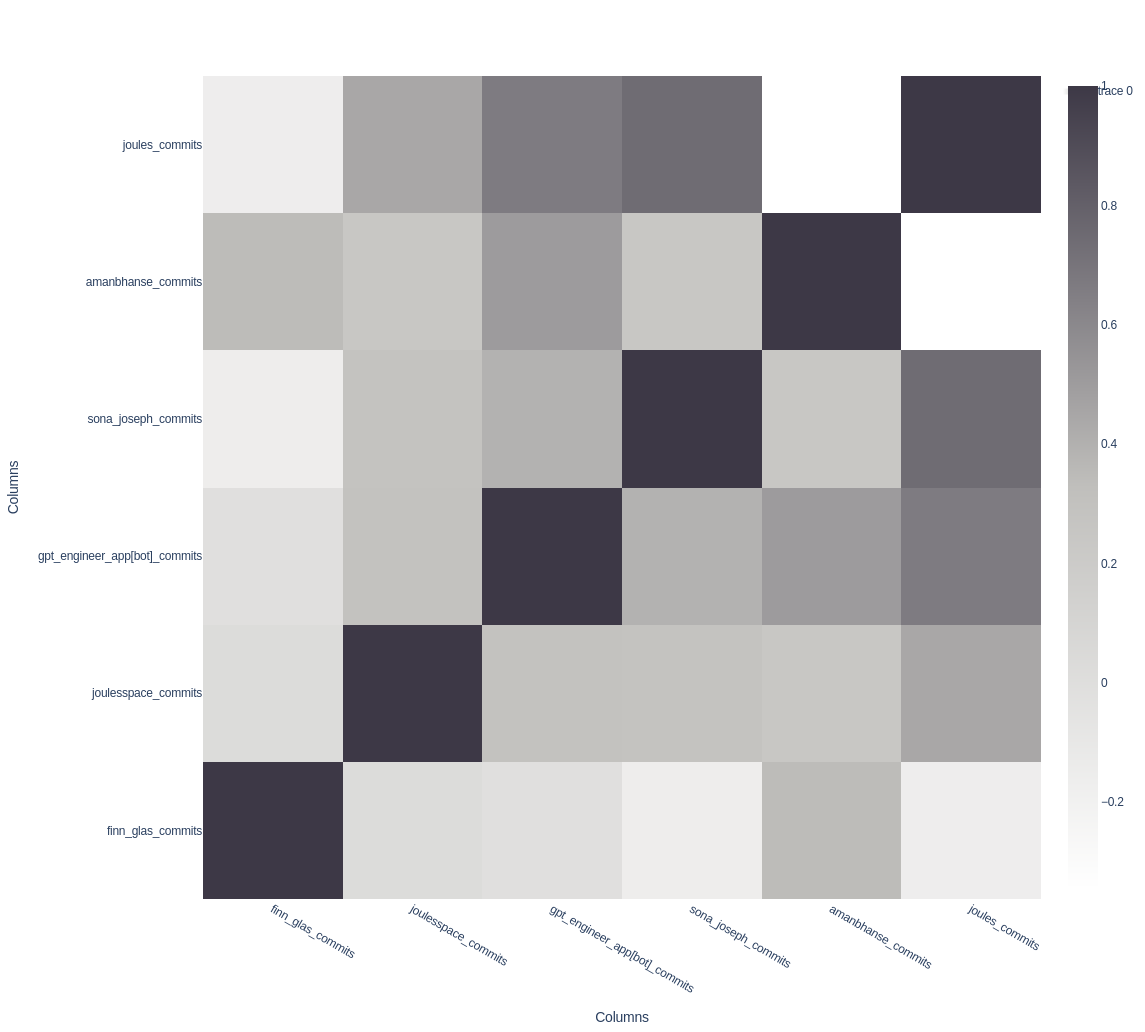
The plot shows the correlation between teammates contributions to the codebase. To the right, you see the black-and-white scale ranging from slightly below 0 (not correlated / inversely correlated) to 1 (meaning exactly equal workload). If you check the gpt-engineer row, you can see it is correlated with every team member except Finn. This is because he did not like the tool and thus did not use it. Aman and Finn seem to have a high correlation, as well as well as Sona and Joules (Julias github account). That "Joules" is Julias github account results in the correlation of the daily commit counts on the two.
You can create a similar plot by creating a corellation plot and selecting your teammates commit count series.
Copy the code below and run it for example in jupyterlab for testing.
import subprocess
import datetime as dt
from collections import defaultdict
from pathlib import Path
import aicuflow
# -------- CONFIG --------
REPO_DIR = "/path/to/repo"
BRANCH = "main"
PATH_FILTER = None # e.g. "src/" or None
FLOW_TITLE = "basic python example"
FILE_NAME = "git_daily_summary.arrow"
BATCH = 500
FILL_EMPTY_DAYS = False # set True if you want zero-commit days
# ------------------------
repo = Path(REPO_DIR).resolve()
if not (repo / ".git").exists():
raise RuntimeError("Not a git repository")
ai = aicuflow.client(email="YOUR_EMAIL", password="YOUR_PASSWORD")
flow = ai.ensure_flow_by_title(FLOW_TITLE)
file = aicuflow.file.byname(ai, flow, FILE_NAME)
cmd = [
"git", "-C", str(repo),
"log", BRANCH,
"--first-parent",
"--numstat",
"--date=iso-strict",
"--pretty=format:@@%H|%an|%ad"
]
if PATH_FILTER:
cmd += ["--", PATH_FILTER]
daily = defaultdict(lambda: defaultdict(lambda: {
"commits": 0,
"add": 0,
import math
import time
import random
import aicuflow
# initialise aicuflow
ai = aicuflow.client(
email="YOUR_EMAIL",
password="YOUR_PASSWORD"
)
flow = ai.ensure_flow_by_title("basic math example")
file = aicuflow.file.byname(ai, flow, "synthetic_preview_data.arrow")
TOTAL_ROWS = 10_000
BATCH_SIZE = 500
buffer = []
start_time = time.time()
for i in range(TOTAL_ROWS):
t = i * 0.01
noise = random.gauss(0.0, 0.15)
sine = math.sin(t)
cosine = math.cos(t)
sine_slow = math.sin(t * 0.1)
sine_fast = math.sin(t * 3.0)
trend = 0.002 * i
scatter = random.random() - 0.5
drifting_noise = noise * math.sin(t * 0.3)
row = {
"index": i,
"time": start_time + t,
"const_one": 1.0,
"linear": i,
"linear_norm": i / TOTAL_ROWS,
"sine": sine,
"cosine": cosine,
"sine_slow": sine_slow,
"sine_fast": sine_fast,
"trend": trend,
"sine_plus_trend": sine + trend,
"noise": noise,
"scatter": scatter,
"sine_noise": sine + noise,
"cosine_noise": cosine + noise,
"drifting_noise": drifting_noise,
"modulated": sine * (1.0 + noise),
"envelope": sine * (0.5 + 0.5 * sine_slow),
}
buffer.append(row)
if len(buffer) == BATCH_SIZE:
file.append(buffer)
buffer.clear()
if buffer:
file.append(buffer)
"del": 0,
"files": 0,
}))
current_day = None
current_author = None
all_days = set()
proc = subprocess.Popen(cmd, stdout=subprocess.PIPE, text=True)
for line in proc.stdout:
line = line.strip()
if not line:
continue
# explicit commit header
if line.startswith("@@"):
_, rest = line[:2], line[2:]
_, author, date = rest.split("|", 2)
day = dt.datetime.fromisoformat(date).date().isoformat()
current_day = day
current_author = author
all_days.add(day)
daily[day][author]["commits"] += 1
continue
# numstat
if current_day is None:
continue
add, delete, *_ = line.split("\t")
s = daily[current_day][current_author]
if add.isdigit():
s["add"] += int(add)
if delete.isdigit():
s["del"] += int(delete)
s["files"] += 1
# determine full day range if needed
days = sorted(all_days)
if FILL_EMPTY_DAYS and days:
start = dt.date.fromisoformat(days[0])
end = dt.date.fromisoformat(days[-1])
days = [(start + dt.timedelta(days=i)).isoformat()
for i in range((end - start).days + 1)]
# build rows — EXACTLY ONE ROW PER DAY
rows = []
for day in days:
ts = dt.datetime.fromisoformat(day).timestamp()
row = {"day": day, "time": ts}
for author, s in daily.get(day, {}).items():
k = author.lower().replace(" ", "_")
c = s["commits"]
row.update({
f"{k}_commits": c,
f"{k}_additions": s["add"],
f"{k}_deletions": s["del"],
f"{k}_files_changed": s["files"],
f"{k}_net_changes": s["add"] - s["del"],
f"{k}_commits_per_hour_avg": c / 24.0,
})
rows.append(row)
# upload sequentially
buf = []
for r in rows:
buf.append(r)
if len(buf) == BATCH:
file.append(buf)
buf.clear()
if buf:
file.append(buf)You find more examples in the python library examples.