Basic Ingress Example
This is a very simple example using the aicuflow python library.
It creates a flow in your user account and streams data to a file in its file manager.
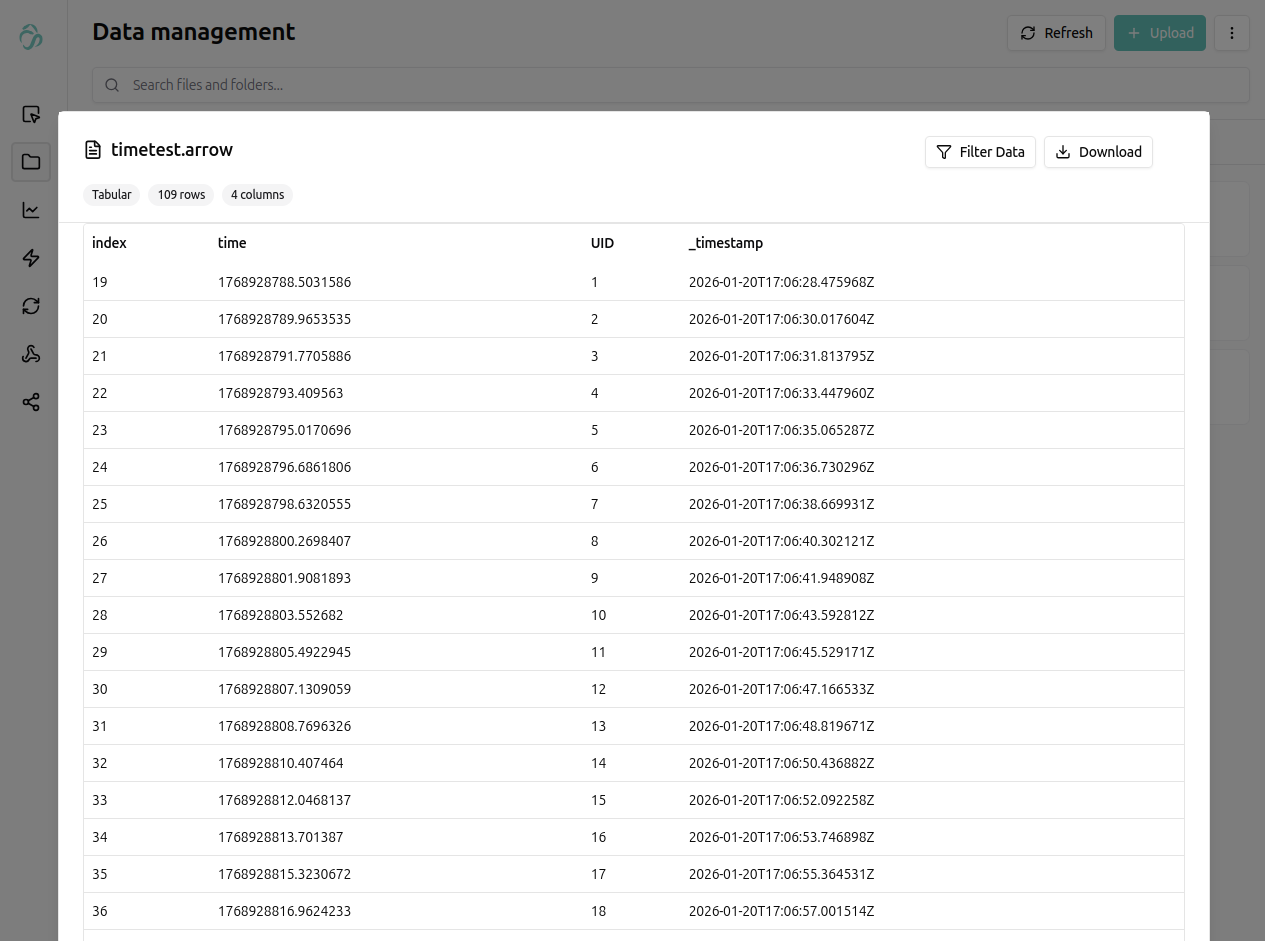
Copy the code below and run it for example in jupyterlab for testing.
import aicuflow, time
# initialise aicuflow
ai = aicuflow.client(
email="YOUR_EMAIL",
password="YOUR_PASSWORD"
)
# initialise project
flow = ai.ensure_flow_by_title("basic python example")
file = aicuflow.file.byname(ai, flow, 'example.arrow')
# collect data
for index in range(100):
file.append(
[
{
"index": index,
"time": time.time()
}
]
)
time.sleep(1)More complex: Audio streaming
Using the above syntax, you can stream arbitrary kinds of data.
The below code is a demo to send audio data in a chunked format:
# pip install sounddevice
# linux: sudo apt install portaudio19-dev
import sounddevice as sd
import time
import base64
# initialise project
flow = ai.ensure_flow_by_title("basic python example")
file = aicuflow.file.byname(ai, flow, "live_audio_stream.arrow")
sample_rate = 16000
channels = 1
chunk_duration = 0.1 # 100 ms chunks
flush_interval = 5.0 # batch upload every 5s
frames_per_chunk = int(sample_rate * chunk_duration)
buffer = []
index = 0
last_flush = time.time()
def audio_callback(indata, frames, time_info, status):
global buffer, index, last_flush
now = time.time()
# raw PCM -> bytes -> base64 (flat, portable, no nesting)
pcm_bytes = indata.tobytes()
audio_b64 = base64.b64encode(pcm_bytes).decode("ascii")
row = {
"index": index,
"time": now,
"sample_rate_hz": sample_rate,
"channels": channels,
# "frames": frames,
"pcm_format": "float32",
"audio_base64": audio_b64,
}
buffer.append(row)
index += 1
if now - last_flush >= flush_interval:
file.append(buffer)
buffer.clear()
last_flush = now
try:
with sd.InputStream(
samplerate=sample_rate,
channels=channels,
blocksize=frames_per_chunk,
dtype="float32",
callback=audio_callback,
):
while True:
time.sleep(1)
except KeyboardInterrupt:
if buffer:
file.append(buffer)You find more examples in the python library examples.